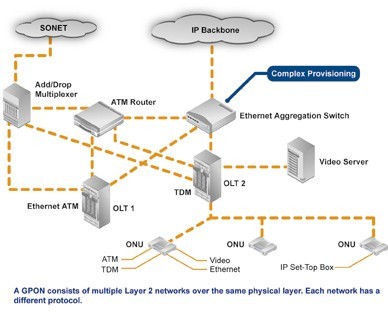
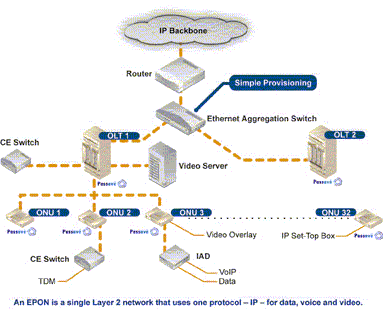
Technical Maturity
Standard
EPON: IEEE802.3ah standard. The standard defines the physical layer of EPON MPCP, the OAM and other related contents. Basic principle for IEEE developing the EPON standard is 802.3 architecture EPON standardization work, minimal expansion of the standard Ethernet MAC protocol.
GPON: ITU-T G.984 series standard. The standard defines the provisions of the GPON physical layer, the TC layer and OAM functions. The GPON standard formulation to consider the support of traditional TDM services, still using the the 125s fixed frame structure to maintain 8K timing continuation. To support ATM multi-protocol, GPON defined an entirely new package structure GEM (GPON encapsulation method), ATM and other protocols can be mixed encapsulation framing.
Core chip
EPON: There are currently 5-6 professional firms providing the EPON core chip (excluding self-designed chip system vendors), these manufacturers have started to chip design and verification during the discussing of the standard, so most of them have launched a second-generation compatible and standard chip when the 802.3ah standard formally promulgated, which can quickly support the EPON system of large-scale deployment.
GPON: Except for the GPON chip, there is no the a professional chip manufacturers launched a commercial GPON core chip that independently designed by themselves. The GPON equipment modules are dedicated to the independent or collaborative development module, no the professional module manufacturers can provide samples, not to mention the mass production.
Multi-service Capabilities And Security
The most questions about EPON is its capacity of transmitting the traditional TDM EPON multi-service. Not to mention the current EPON equipment manufacturers to use the patented technology of the TDM over Ethernet provides TDM EPON single segment of the business of transmission channels, from the test results, and its performance is completely meet 1.5ms delay index requirements, in full compliance with the traditional TDM services standards. Even in ordinary Ethernet devices, now it also can use a variety of standard PWE3 (pseudowire emulation edge to edge) devices to provide cross-network segment, the end-to-end transparent traditional point-to-point TDM channel. With the dwindling proportion of traditional TDM traffic using packet switching technology TDM services asylum growing packet networks, will undoubtedly be a more economical means. Security, EPON standard AES-based encryption technology, with the security of GPON.
QoS
In QoS, EPON defines eight priority queues, DBA algorithms are also taken into account the priority queue bandwidth allocation strategy and fairness and other issues. IP a priority or Ethernet priority packet can be easily mapped to eight priority queues, and then through the DBA algorithm guarantees the transmission bandwidth and delay, QoS requirements fully meet the needs of different business . The GPON OLT detects the traffic load of each CONT-T for prediction / analysis ONU business flow and network congestion and allocate resources to each CONT-T, according to the network conditions, but does not involve the VP / VC, or Port_ID QoS. VP / VC, or Port_ID provide QoS guarantees by the corresponding mechanisms at both ends of the ATM / GEM client.
For different QoS requirements of the business, GPON by to use pointers arrangements ONU using the different transmission mode to achieve: to adjust its authorized bandwidth and authorization cycle to guarantee the bandwidth and latency requirements of the business. In fact, how to guarantee QoS EPON and GPON implementation mechanism is essentially the same. OAM including the GPON bandwidth authorized allocation, DBA, link monitoring, protection switching, key exchange, and various alarm functions. Itself from the standard point of view, the GPON standard defined richer OAM information than the the EPON standard definition, but from the actual equipment of view, both provide the functionality and not much difference, the current EPON equipment can also provide these features.
To sum up, in terms of QoS, multi-service bearer security, the current EPON products are similar with GPON standard specified. But the cost per unit bandwidth is much lower than the EPON, besidesl EPON technology is more mature, earlierbe accepted by the market, and earlier enter the commercial stage in large-scale. The next generation network is a packet-based network, Ethernet as the absolute mainstream bearing platform of the packet network has become an indisputable fact. The user network interface in the future is certainly an Ethernet interface, the Ethernet interface on the MAN will surely be ubiquitous. Using Ethernet technology to connect the Ethernet interface on both sides will be a very natural thing.