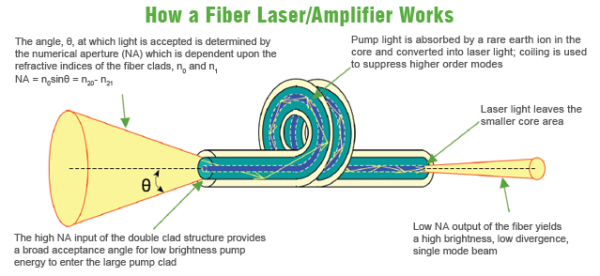
What is fiber laser? The world's first laser beam is produced in 1960 by the use of flashbulb stimulating ruby crystalline grain. Limited by the thermal capacity of the grain, the pulsed beams is short and the frequency is very low. Although the instantaneous pulse peak can reach up to 106W, it still belongs to low energy output.
Source:tamu.edu
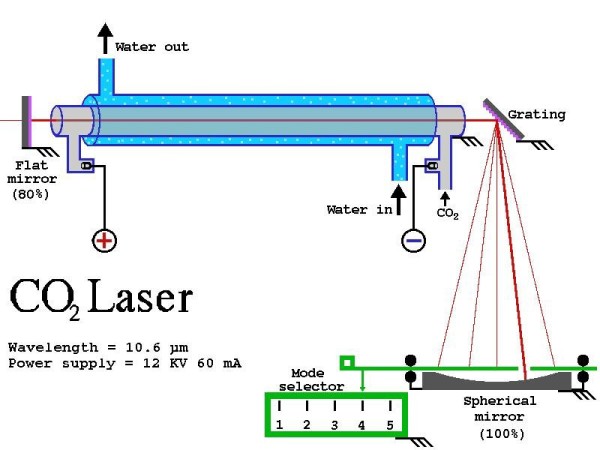
Laser technology adopts the beams of light generated by the reflection of laser from polariscope and congregates the beams in focusing device to generate beams with enormous energy. Once the focus is approaching, the workpieces will be melt or vapored in some milliseconds. This opens up a new welding application domain for high power CO2 and high power YAG laser. The key of laser welding equipment is high power laser, including solid laser and gas laser. Solid laser is the so called Nd:YAG laser. Nd is a rare earth elements and YAG represents Yttrium Aluminum Garnet, with similar crystal structure as ruby. The wavelength of Nd:YAG laser is 1.06μm. It can produce beam transmitted by fiber, so it can simplify beam delivery system, which is suitable in flexible manufacturing systems and remote working as well as high welding precision workpieces. Nd:YAG laser of 3-4 KW output is commonly used in automobile industry. Gas laser is the so-called CO2 laser. Its working medium is molecule gases which can generate iraser of 10.6μm in average. It can work continuously and output very high power; the standard laser power is between 2-5 KW.
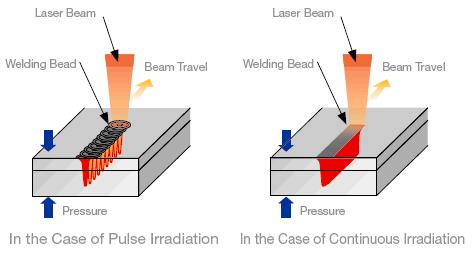
The major traits of laser welding are as following:
- The welding is fast and deep with little deformation.
- It can work in room temperature and disparity conditions with simple equipment and device. For example, the laser beam will not offset; laser welding can be really carried out in vacuum, air or any gas environment, or even through glass or any transparent material.
- It can weld refractory materials as titanium and quartz and anisotropic materials with good effects.
- When welding, depth-to-width ratio can reach to 5:1 and the highest can reach up to 10:1.
- It can applied in microwelding. Slight flare can be generated by focused laser beams which can positioning precisely and be applied in mass automatic production of micro and small workpieces' installation and welding.
- It is flexible in welding areas that is difficult to access. Especially in recent years, the adoption of optical fiber transmission in YAG laser processing technology has greatly promoted the popularization and application of laser welding technology.
- Beam split is easy to be realized by time and space and multiple beam can be processed all at once, providing conditions for more precise welding.
However, there are some limits of laser welding:
- It requires high assembly accuracy for weld and it should has no obvious deviation of beam on workpieces. It is because that the flare is too small and the welding line is too narrow. If the assembly accuracy and beam position cannot meet the requirements, it is easy to make weld defect.
- The cost and initial investment on laser and the relevant systems are high.
Resource : avio
DK Photonics – www.dkphotonics.com specializes in designing and manufacturing of high quality optical passive components mainly for fiber laser applications such as 1064nm high power isolator, Cladding Power Stripper, Multimode High Power Isolator, pump combiner,1064nm Band-pass Filter,(6+1)X1 Pump and Signal Combiner, PM Circulator, PM Isolator, optical Coupler. More information, please contact us.